Delighted to share our latest research has been published in Additive Manufacturing, Elsevier!
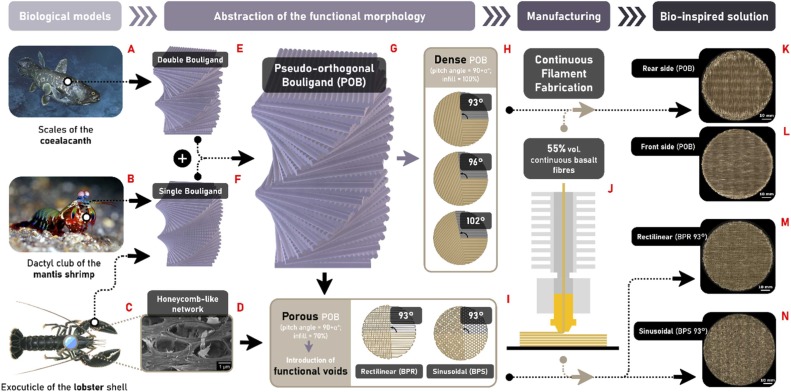
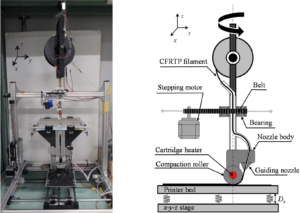
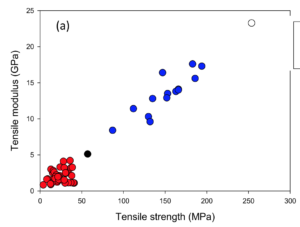
In this work, the energy dissipation principles of several Bouligand architectures found in structures developed by coelacanths, mantis shrimps and lobsters serve as design principles for 3D-printed efficient energy-dissipative panels, made of continuous basalt fibres and a thermoplastic matrix to simulate lunar based/recycled Earth-based materials. The influence of the stacking sequence, infill pattern and infill density are explored. The different panels designed are tested under non-perforating low-velocity impact (10 m.s-1, 50 J), their impact behaviour, damage mechanisms and energy dissipation efficiency are studied in depth. Results highlights that the proposed panels compete and, in some aspects, outperform conventional laminates. Additionally, introducing functional voids enables to increase the energy dissipation while reducing the mass, opening the way to lightweight protective structures in space and on the Moon.
All co-authors gratefully acknowledge the European Space Agency and Institut Carnot Arts for the financial support.
Authors P.L. Pichard, L. Maheo, J. Dirrenberger, M. Castro, U. Lafont, A. Le Duigou
Read the full paper in open access here: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2025.104875